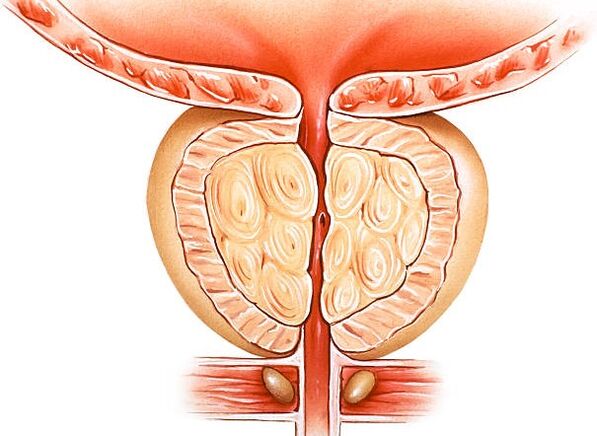
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate, a gland that produces the liquid part of the semen. This is the most common disease of the reproductive system in mature men. Acute bacterial prostatitis is a relatively rare disease, its frequency does not exceed three percent of all inflammatory processes in the prostate.
Causes of acute prostatitis
The main cause of acute prostatitis in men are bacteria, some of which are part of the normal microbiota in the body, or live permanently on the skin, in the intestines. Entering the tissues and ducts of the prostate, they cause acute inflammation.
The infection can enter the prostate in two ways:
- ascending canal - bacteria with urethritis, cystitis, after cystoscopy enter the prostate.
- hematogenous - microbes enter the prostate with blood flow from distant foci of acute and chronic infection - boils, carbuncles, sinusitis, diseased teeth and tonsils.
In addition to bacteria, stagnation of prostate secretions and stagnation of venous blood are important, which develop during irregular sexual activity with infrequent sexual intercourse, with long-term restrictions on mobility, especially in a sitting position and wearing tight underwear.
The gland consists of two parts - the follicles in which the secretion is created and the excretory ducts through which the liquid part of the semen enters the urethra. Depending on which part of the prostate is inflamed, there are different forms of acute prostatitis in men that are treated with different methods.
Signs of acute prostatitis
The symptoms of acute prostatitis depend on the shape and severity of the inflammatory process. Doctors distinguish three forms:
- catarrhal.The main symptoms are urinary incontinence. The ducts become inflamed, the prostate enlarges and blocks the urethra, causing the urination to lengthen, followed by pain and a burning sensation in the urethra. There are nocturnal urges, the patient suffers from insomnia.
- follicular.As the process progresses, the tissues of the follicles begin to fertilize. Urinary disorders are accompanied by pain in the perineum, radiating to the anus, the temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- parenchymal.The follicles continue to fertilize, creating a large number of small abscesses. Difficulty urinating, they become sharply painful, pains appear during the act of defecation. The temperature rises to forty, in the groin, perineum, sacrum - sharp pains.
Diagnostic tests
The urologist makes the diagnosis based on a comprehensive study that includes:
- Rectal examination.The urologist inserts a finger into the patient's anus and feels the gland, finds an increase in volume and pain, and concludes that there is an inflammatory process.
- General urine analysis.Leukocytes, blood, bacteria and proteins are determined in the analysis of urine. These are nonspecific indicators of urinary tract inflammation; they cannot be used to infer a particular site of inflammation.
- Bacteriological analysis of urine.Urine culture for sterility allows you to isolate the microbes that caused the inflammation, determine their type, resistance and sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Prostate ultrasound.Ultrasound examination shows a change in size, indicates nodules, formations, abscesses.
- MRI or CT of the pelvis.It is performed as a preparation for surgery or for differentiation with prostate tumors.
- Blood test for PSA.Prostate specific antigen is a protein secreted by the prostate. Its content increases in prostate diseases - prostatitis, adenomas and malignant prostate tumors. The analysis is performed for the differential diagnosis of tumors, because the PSA values in cancer are much higher than in prostatitis.
Complications of acute prostatitis
If the proper treatment of acute prostatitis is not started in time, it can lead to the development of the following complications:
- Prostate abscess.If prostatitis is not treated, sooner or later small abscesses merge into one large one, called an abscess. This complication is treated immediately, by opening the prostate and carefully clearing the pus from there.
- Inflammation of the paraprostatic venous plexus. Inflammation of the prostate can spread to the surrounding veins. A large number of bacteria released into the bloodstream will lead to a systemic inflammatory response - sepsis - which can be fatal.
- Paraprostatitis.It occurs when an abscess penetrates the surrounding prostate tissue. Treat only immediately.
- Transition to a chronic form.Acute prostatitis without treatment becomes chronic, which requires a course that lasts several years. Fifty percent of patients with chronic prostatitis develop mental disorders that require correction with antidepressants and tranquilizers.
What to do with acute prostatitis
A patient with an attack of acute prostatitis needs urgent hospitalization. Treatment of acute prostatitis should take place in a hospital and includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and restorative agents.
Antibacterial therapy includes broad-spectrum agents and is prescribed for a longer period - from fifteen to thirty days, until the bacteria are completely destroyed. For acute prostatitis, doctors usually use the following antibiotics and antibacterial drugs:
- fluoroquinolones- levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin;
- trimethoprim;
- doxycycline;
- cephalosporins- cefotaxime, ceftriaxone.
In addition to antibiotics for acute prostatitis, the following medications are used:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac) - help relieve pain;
- bioregulatory peptides (prostate extract, vitaprost, prostatylene) - used in the form of suppositories. The prostate not only produces the liquid part of the semen, but also performs a regulatory function by releasing hormones. Suppositories help to compensate for the lack of hormones and avoid the complications associated with it.
Don't self-medicate - it's dangerous! Do not use folk remedies such as prostate massage - secretions and pus, which are once in the blood, cause blood poisoning, which can be fatal. If you find signs of acute prostatitis, call an ambulance immediately or see a doctor.
Sex with acute prostatitis is contraindicated. First, severe pain in the perineum and lower back, high fever, absolutely do not expose sexual intercourse. Second, the partner is at risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
Prevention of acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is much easier to prevent than to cure. Just notice a few important things:
- conduct thorough personal hygiene, treat cystitis and urethritis on time;
- have regular sex to avoid stagnation of prostate secretion;
- avoid sexually transmitted diseases;
- timely treat ulcers, carbuncles, monitor dental health;
- wear loose cotton underwear;
- ensure yourself enough physical activity to avoid stagnation in the veins of the prostate.
Treatment of prostatitis should be carried out under strict medical supervision. The specialist develops an examination program and compiles an individual diagnostic scheme.
It is important to consult a doctor at the first suspicion of pathology. Lack of attention to symptoms or self-medication can significantly complicate the situation. Timely and professional medical help will help cope with the disease and prevent complications.
Symptoms and causes of prostatitis
As a rule, when talking about the treatment of prostatitis, they imply a chronic phase of pathology. This is due to the fact that the acute phase lasts only a few days and often does not cause serious concern in men. As a result, the inflammatory process becomes chronic, and the treatment of prostatitis is significantly delayed.
Acute prostatitis can be recognized by the following signs:
- pain in the perineum and scrotum,
- cramps in the lower abdomen
- weakening of the erection,
- lack of voluntary erection in the morning.
Such symptoms may occur all at once or all at once. After a few days, they disappear or decrease significantly. This is exactly the danger of disease. In the absence of qualified help, prostatitis becomes chronic. This phase is characterized by:
- increased urge to urinate,
- reducing the amount of urine excreted,
- weakening of the jet during urination,
- erectile dysfunction,
- pain in the small pelvis, perineum.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to visit a doctor. In our clinic, a urologist at Leninski will precisely determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
Determining the etiology of prostatitis is one of the most important tasks when choosing a course of therapy. There are several main causes of the disease:
- sexually transmitted infections - chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis and others,
- bacteria - enter the prostate through the urethra, blood or lymph flow,
- hypothermia - causes inflammation of the prostate which, as in other cases, quickly becomes chronic.
All the necessary examinations to determine the cause and treatment of prostatitis can be done in our clinic. The examination program is made by the urologist individually.
Diagnosis of the disease
Among the mandatory methods for diagnosing prostatitis are:
- general urine analysis,
- microscopic examination of prostate secretions,
- Prostate ultrasound.
In accordance with the individual clinical picture, the urologist may prescribe additional examinations. If you suspect the sexually transmitted nature of prostatitis, testing for sexually transmitted diseases on Leninsky Prospekt is recommended. Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the specialist compiles a treatment regimen for prostatitis.
Complex therapy
Prostatitis is often treated with conservative methods. The basis is antibiotic therapy. With the help of antibiotics, pathogens are removed, and inflammation of the prostate is removed. Modern drugs penetrate well into the prostate tissue, eliminating the main cause of pathology. In addition, the doctor may prescribe alpha-blockers, hormones, muscle relaxants.
Another effective technique is prostate massage. It restores the patency of the canal, improves blood circulation in the prostate and increases its tone. It is most commonly used in the treatment of bacterial prostatitis, the presence of pelvic pain syndrome.
The duration of the course depends on the individual picture of the disease. It is important that the treatment of prostatitis in the clinic is not aimed at alleviating the symptoms, but at eliminating the main cause of the pathology. This approach allows you to get rid of chronic diseases and prevent relapses.